Mastering Your Vehicle's Performance: The Ultimate Guide to the Gas Fuel System
🎁 A Personal Gift For My Readers
To support your project, I've secured an exclusive 8% OFF for you.
Simply paste the code at checkout.
💡 Use the savings to grab your extra fittings, oil lines, or connectors for free!
Whether you are restoring a classic muscle car, prepping an LS swap, or optimizing a street machine, understanding your fuel system is the foundation of automotive excellence. A high-performance gas fuel system does more than just move petrol from point A to point B; it ensures precise pressure regulation, contamination-free delivery, and ultimate reliability under heat and stress.
In this pillar guide, we will break down the mechanics of fuel delivery, answer common questions like 'how does a gas tank work?', and help you choose the right upgrades from the EVIL ENERGY Fuel System Collection.
The Heart of Storage: How Does a Gas Tank Work?
Many enthusiasts ask, 'How does a gas tank work?' or 'How do gas tanks work?' beyond just being a hollow container. Modern gas tanks are sophisticated components designed to manage fuel sloshing, venting, and pressure.
How Does a Fuel Tank Work in Modern Vehicles?
-
Storage & Baffling: Inside a performance gas fuel system, tanks often feature baffles to prevent fuel starvation during hard cornering.
-
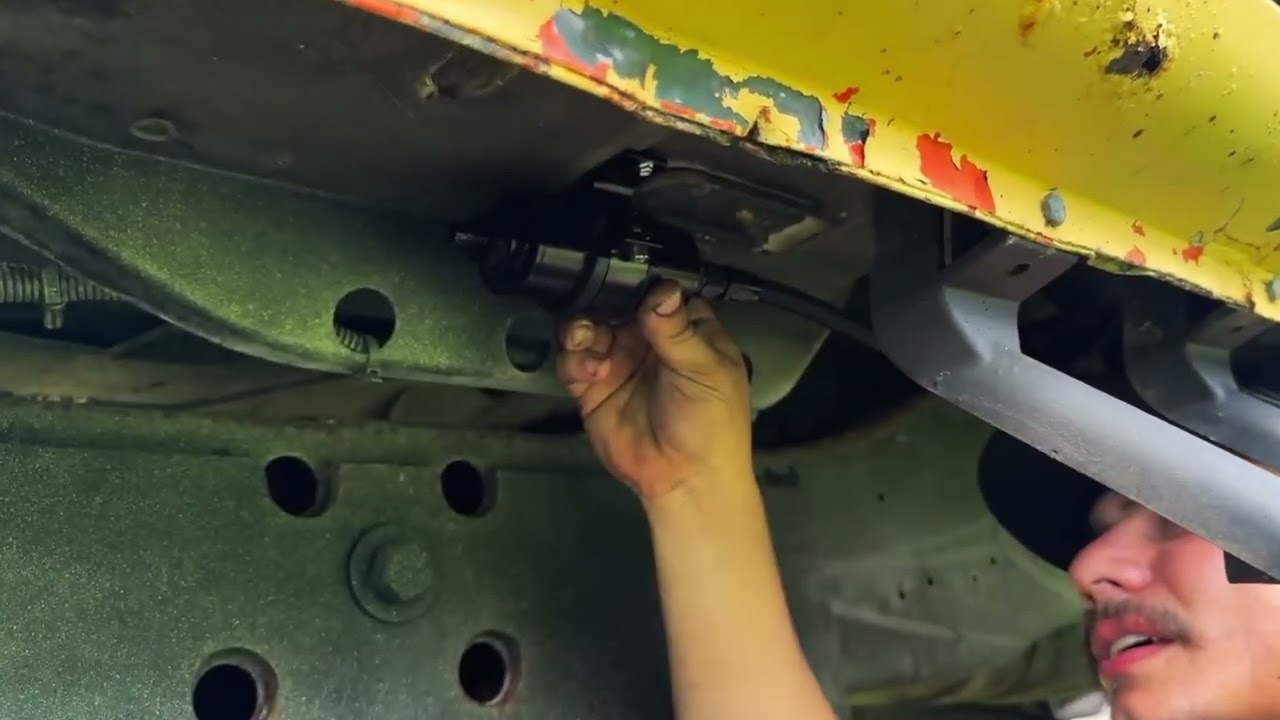
The Pickup Mechanism: This is where the fuel pump (in-tank or external) draws gas to send it down the lines.
-
Venting & Evaporation: To prevent the tank from collapsing or expanding due to temperature changes, the fuel system uses a venting system to manage vapors.
If you are looking for a more specialized setup, such as for racing or off-roading, you might consider a fuel cell. Learn the specifics in our Fuel Cell Gas Tank Guide and discover How Does a Fuel Cell Work? to see if it’s right for your project.

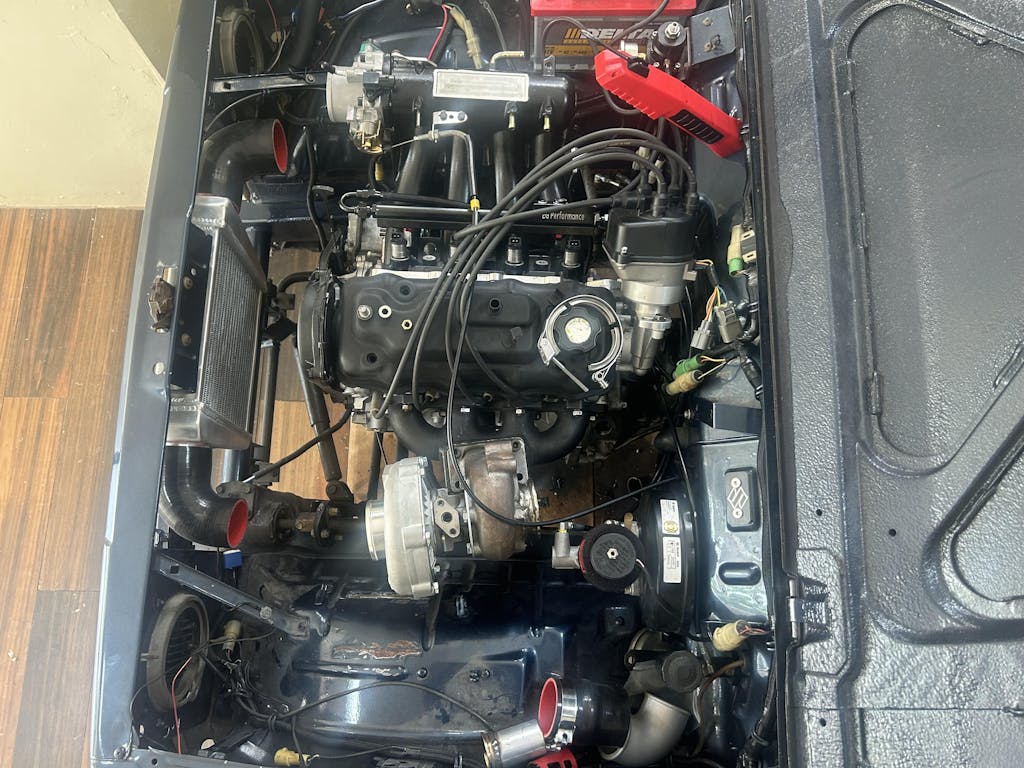
Key Components of a High-Performance Fuel System
To achieve maximum efficiency in your gas fuel system, every part must work in harmony.
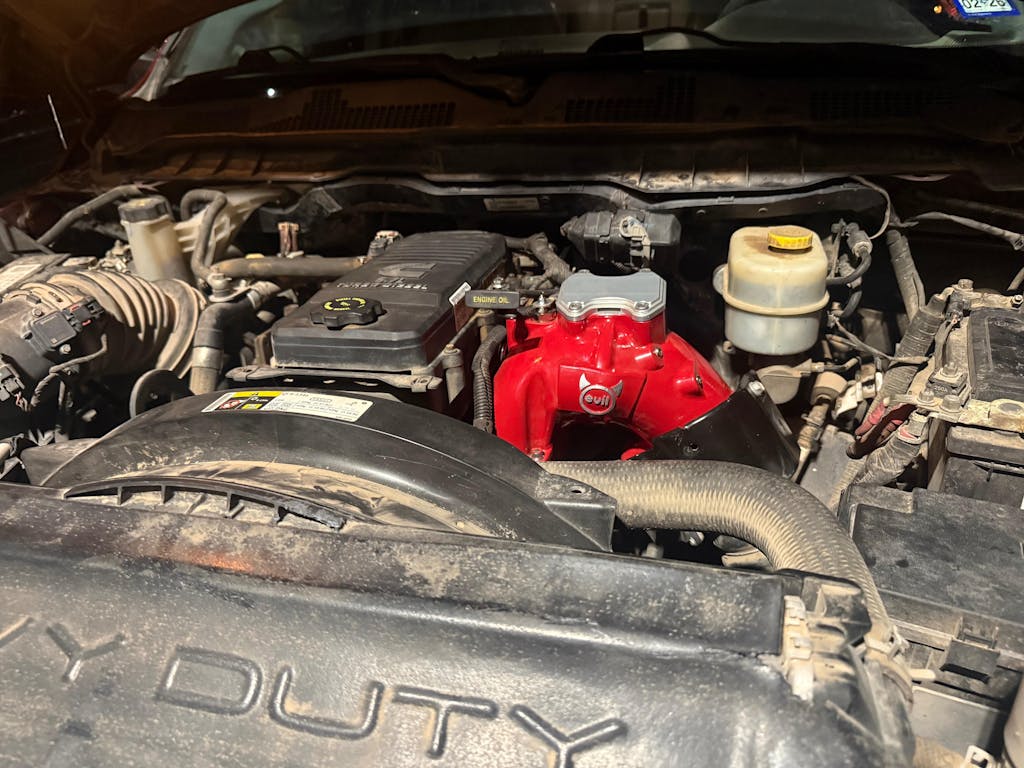
Fuel Pumps: The Pulse of the System
The fuel pump is the heart of the fuel system. Choosing between an in-tank or external pump depends on your horsepower goals.
-
Troubleshooting: Having issues? See our tips on how to reset the fuel pump relay.
Carburetors: The Classic Choice
-
Comparison: 650 CFM vs 750 CFM Carburetor
Fuel Lines and Fittings
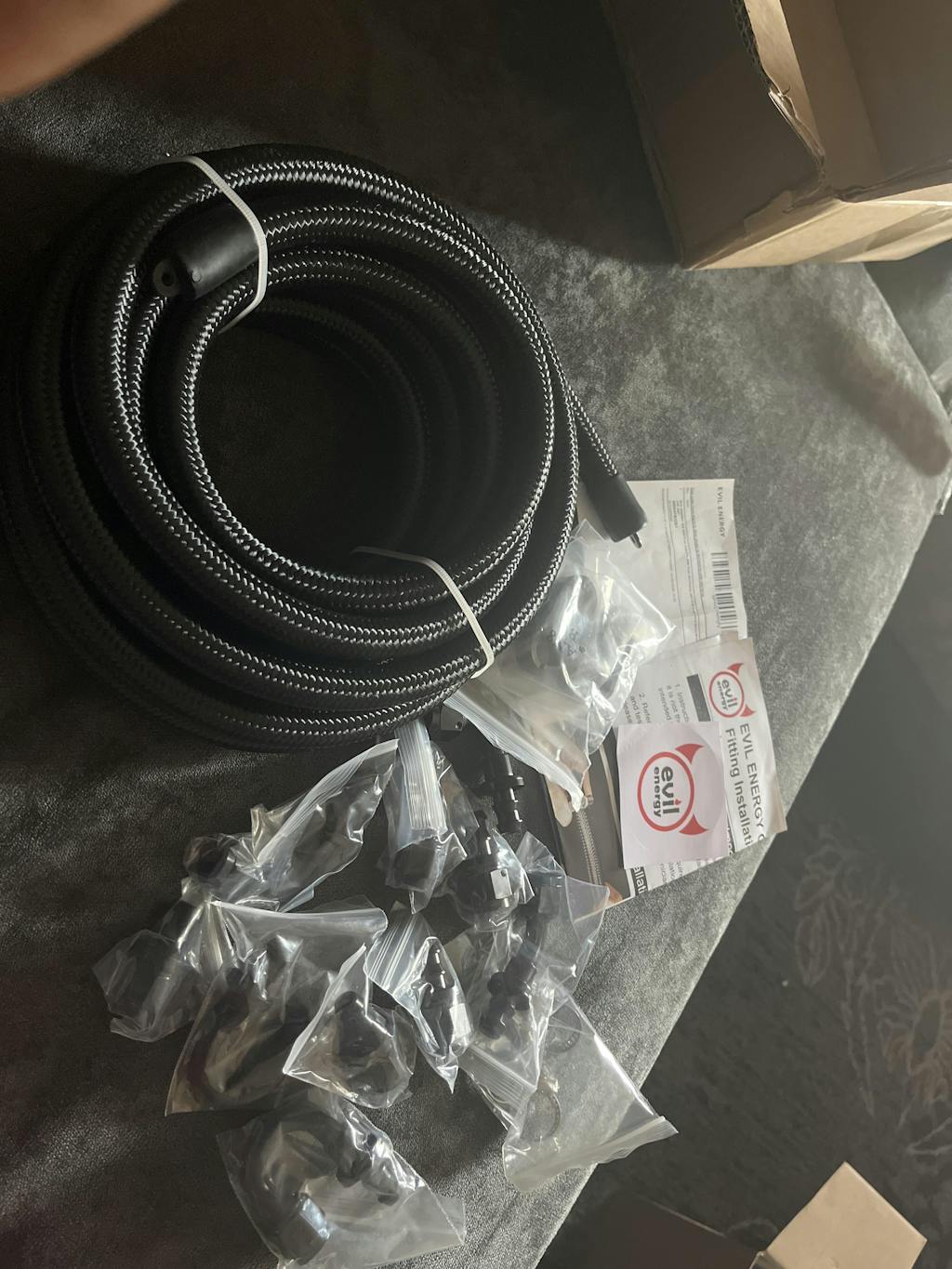
A high-performance gas fuel system is only as strong as its weakest connection. Using 15 Gallon Fuel Cells & PTFE Fuel Lines ensures that your lines can handle modern ethanol-blended fuels without degrading.
Troubleshooting Your Gas Fuel System
To keep your fuel system in top shape, you must recognize the warning signs of component failure.
| Symptom | Potential Cause | Recommended Action |
| Engine Hesitation | Clogged filter or weak pump | Check Fuel Pump Replacement Costs |
| Hard Cold Starts | Fuel pressure loss or carb issues | Tune your Carburetor |
| No Fuel Delivery | Electrical or Relay failure | Reset Fuel Pump Relay |
| Fuel Odor/Leaks | Line degradation (Ethanol damage) | Upgrade to PTFE Fuel Lines |
Visualize Your Build
Understanding the routing of your lines and the placement of your filters can be tricky. We’ve created The Ultimate Visual Guide to Your Car’s Fuel System & Tank Anatomy to help you map out your project with confidence.
Conclusion: Build It Right with EVIL ENERGY
Upgrading your gas fuel system is an investment in your vehicle’s heart. By answering 'how does a gas tank work?' and choosing components that handle modern fuel chemistry, you protect your engine and boost performance.
Ready to upgrade? From high-flow pumps to AN fittings and PTFE lines, find everything you need in the EVIL ENERGY Fuel System Collection.
The Ultimate Gas Fuel System FAQ: Performance, Mechanics, and Upgrades
Building a reliable high-performance vehicle starts with the heart of its delivery: the fuel system. Whether you are tackling a classic restoration or a modern engine swap, understanding the plumbing and physics of your gas fuel system is critical for both safety and power.
In this guide, we answer the most common questions enthusiasts ask when designing, maintaining, or upgrading their vehicle's fuel delivery components.
Q1: How does a gas fuel system work in a modern performance car?
A gas fuel system is a pressurized circuit designed to store, filter, and deliver fuel to the engine. It starts at the tank, where a pump sends fuel through high-pressure lines. A regulator maintains the exact PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) required, while filters remove contaminants that could clog injectors or carburetors. In performance builds, the fuel system must be capable of increasing flow instantly to match high-RPM air intake.
Q2: How does a fuel tank work to prevent engine sputtering?
If you’ve ever wondered how does a fuel tank works during hard cornering, the answer is internal baffling. Performance tanks feature vertical walls (baffles) that keep the fuel trapped around the pickup tube. Without these, fuel would slosh to one side, causing the pump to suck in air—a phenomenon known as fuel starvation that leads to engine hesitation or damage.
Q3: How do gas tanks work in terms of pressure and venting?
A gas fuel system cannot be a completely sealed box. As the fuel pump draws gas out, air must replace it to prevent a vacuum from collapsing the tank. Conversely, as fuel warms up, it expands and creates vapor. Modern tanks use specialized vent valves that allow the tank to 'breathe' while preventing raw fuel from leaking out during aggressive driving or a rollover.
Q4: What is the difference between a Return and a returnless fuel system?
-
Return System: Uses two lines. One sends fuel to the engine, and the other returns unused fuel to the tank. This is the gold standard for performance because it keeps fuel moving and cooler.
-
Returnless System: Uses a single line. The pump or an internal regulator manages the pressure. While simpler to plumb, it is more prone to 'heat soak' in extreme racing conditions.
Q5: Why is PTFE plumbing better for a high-performance fuel system?
Modern pump gas often contains ethanol (like E10 or E85), which is highly corrosive to traditional rubber hoses. Gas fuel system upgrades now almost exclusively use PTFE (PolyTetraFluoroEthylene) lines. PTFE is chemically inert, meaning it won’t break down, and it acts as a vapor barrier to prevent that 'gasoline smell' in your garage.
Q6: How does a fuel tank work when using an external fuel pump?
When using an external pump, the fuel system relies on gravity. Since most external pumps are excellent at 'pushing' but poor at 'pulling' fuel, they must be mounted lower than the fuel tank. The fuel flows out of a 'sump' at the bottom of the tank into the pump, ensuring a constant prime.
Q7: How do I know if my fuel system is failing?
Common symptoms of a failing gas fuel system include:
-
Sputtering at high speeds: Indicates the pump cannot maintain flow.
-
Hard starts: Suggests the system is losing 'prime' or pressure overnight.
-
Loss of power: Often caused by a clogged fuel filter restricting the fuel system under load.
Q8: How does a fuel tank work in a 'Fuel Cell' configuration?
A fuel cell is a specialized version of a gas tank used in racing. It often contains an anti-slosh foam that divides the fuel into thousands of tiny pockets. This not only prevents fuel from shifting during high-G turns but also prevents a massive explosion in the event of a tank puncture.
Q9: Does the size of the fuel line matter for performance?
Absolutely. If your fuel lines are too small, they act as a bottleneck for your fuel system. Most 500-600 horsepower builds require at least a -6AN or -8AN line size to ensure the volume of gas can keep up with the engine's demand.
Q10: What is the most important maintenance task for a gas fuel system?
The most critical task is regular filter inspection. A high-performance fuel system usually has two filters: a coarse 'pre-filter' to protect the pump from large debris and a fine 'post-filter' (usually 10 microns) to protect the injectors. Replacing these annually ensures your pump doesn't have to work overtime to push fuel through a restriction.





![[20FT] EVIL ENERGY PTFE Fuel Line Kit, complete black hose & fittings set, 180-day return](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/Test-2025-Evilenergy-125598065_533x.png?v=1742144807)
![[16FT] EVIL ENERGY PTFE Fuel Line Kit, black braided hose, fittings, free shipping & return](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/Test-2025-Evilenergy-125598171_533x.png?v=1742144807)
![CPE Fuel Line[25FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/25FTCPE_FuelLine_533x.png?v=1735220649)
![CPE Fuel Line[20FT]](http://www.ievilenergy.com/cdn/shop/files/20FTCPE_FuelLine_533x.png?v=1735220649)